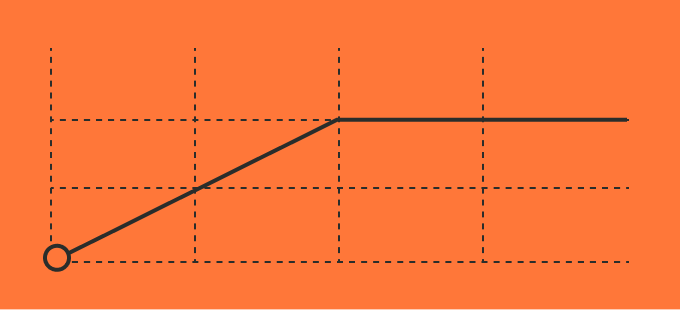
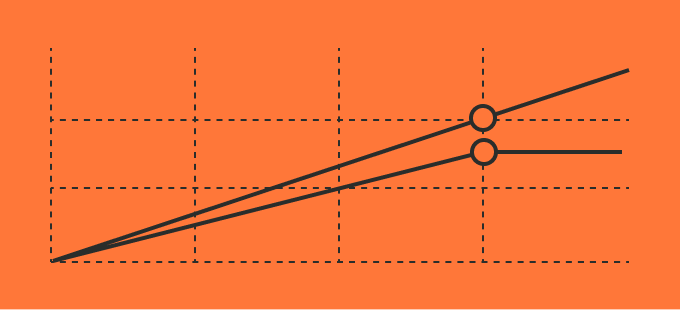
- Scaled company more concerned with expanding accounts
- PLG models focused on increasing adoption
Net Revenue Retention
An NRR-focused compensation plan makes most sense for scaled organizations or those with product-led growth (PLG) strategies. In this model, you’re incentivizing AMs to grow their existing book of business versus retaining every customer.
When to use this plan?
Why use a NRR plan?
Focuses on keeping the dollars you have, or finding upsells with renewing customers to make up for churned customers
Build the Net Revenue Retention Plan
Like this plan? Sign up for QuotaPath to customize this plan with your variables.
Forecast earnings & plan performance
See potential earnings based on your inputs and goal attainment progress.
Test plan proposals
Connect your sales source of truth to test previous sales cycle data against your drafted plan.
Streamline plan management
Assign the plan to your team and automate sales commission calculations. Be confident that your team is being paid fairly and accurately.
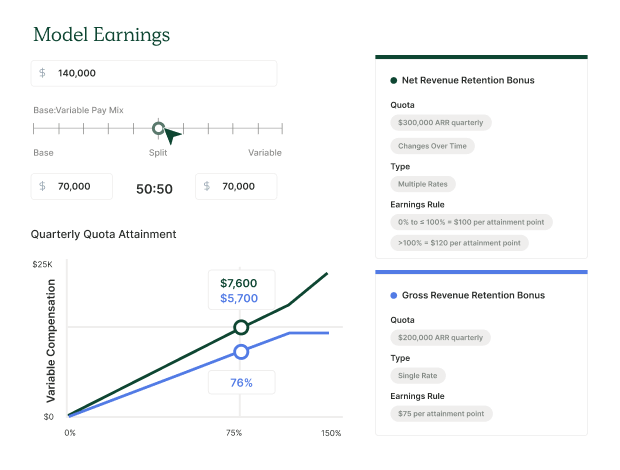
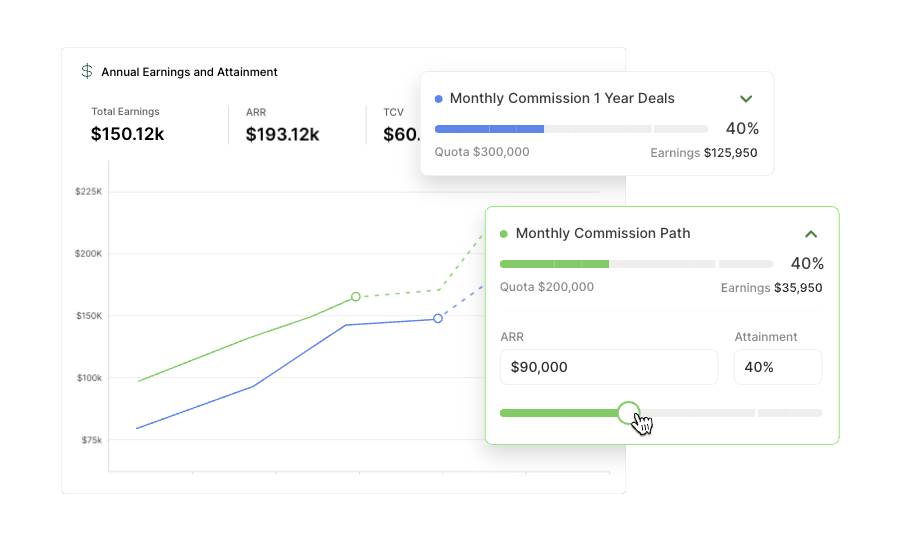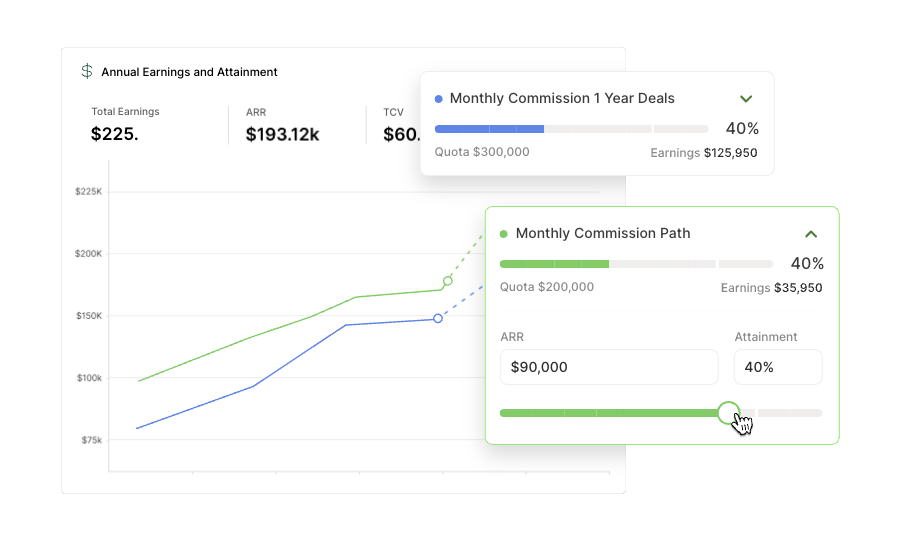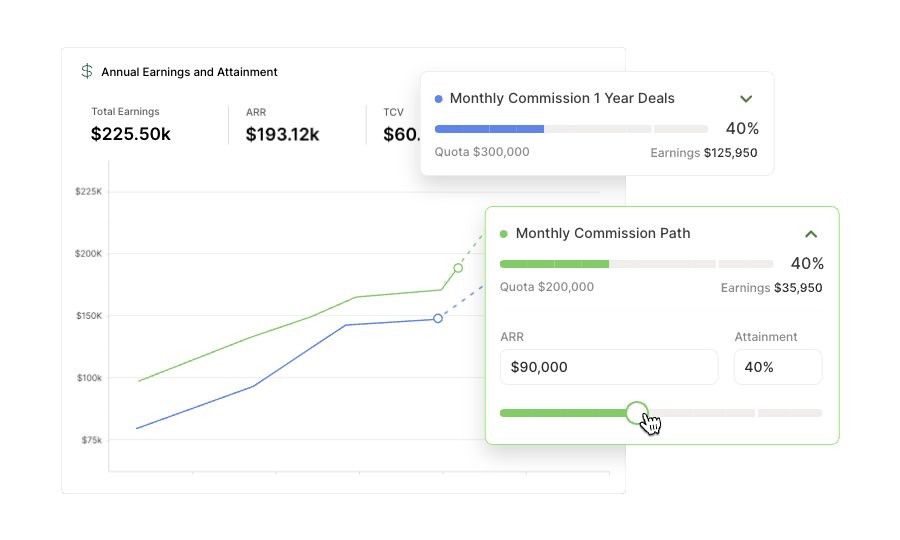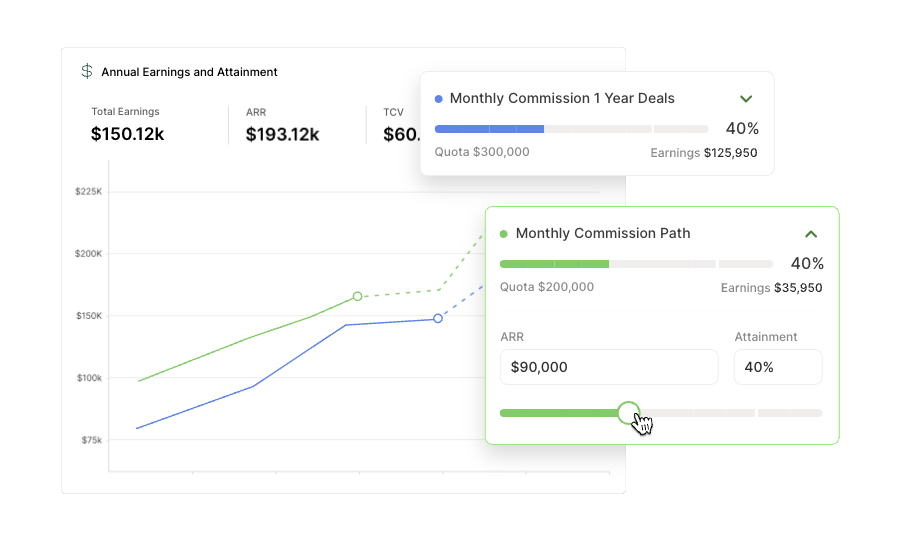
How to adjust this compensation plan
To customize this plan, input the following variables.
Pay Mix
Pay mix combines the base salary and on-target variable pay ratio. You might see 50/50, 60/40, or 70/30 pay mixes for account manager roles.
Company Revenue
Revenue is a company’s total income from its primary operations. In SaaS, annual recurring revenue is a crucial metric for many organizations.
Book of Business
This is the portfolio of assigned customers they are responsible for managing and growing. Some focus on the number of customers, while others measure the amount of revenue.
Quota
This will vary depending on the industry or company but will be based on a retention percentage that is often less than 100%.
Quota Period
For account managers, the most common quota period is quarterly, which is the time interval between the quota resetting.
How much do account managers make?
SaaS account managers reported an average salary of $72,000, via data from Built In. When factoring in commissions, they reported average earnings of $40,000, for a total OTE of $112,000. Note that this number varies based on location, industry, level, and how the organization sets up its commission structure.
What should the pay mix be for account managers?
An 80/20 base salary to variable compensation split is most common amongst account management teams. You may also see a 70/30 or a 60/40 split.
This is unlike sales compensation plan examples because the role of an account manager requires a lot more time supporting customers and responding to calls that are not renewal/expansion related.
What are the best compensation plans for account managers?
The best compensation plans for account managers are both simple in design and impactful as far as driving the right behaviors.
We recommend the Gross Revenue Retention AM compensation plan if you want your AMs solely focused on renewing the existing customer base.
Now, if you want your AM team to focus on keeping the dollars you have or finding upsells with renewing customers to make up for churned customers, this Net Retention Revenue compensation plan is more suitable.
For the best of both worlds, combine the two in our Gross & Net Revenue Retention AM Comp Plan. In this comp plan, you split the total business between GRR and NRR so that the number doesn’t change quarter-over-quarter.
How do you calculate GRR vs NRR?
GRR and NRR are metrics used to measure revenue retention in a SaaS company.
GRR measures total revenue retained from the customer base without considering expansion revenue. To calculate GRR, use the following formula:
GRR = (Total revenue from current customers at end of period – Total revenue from current customers at the beginning of period) / Total revenue from current customers at the beginning of period
NRR measures revenue retained from the customer base after accounting for both churn and expansion revenue. To calculate NRR, use the following formula:
NRR = ((Total revenue from current customers at end of period – revenue from churned customers) / Total revenue from current customers at the beginning of period) x 100
While GRR is useful for understanding how well a company is retaining its customer base, NRR provides a more complete picture by factoring in the revenue generated from existing customers. NRR can help companies understand the impact of customer expansion on their overall revenue and identify opportunities for growth and customer success.
What account management comp plan should I use?
To select a compensation plan for account managers, it is important to first understand your business objectives and goals — ie: GRR or NRR. You’ll want to align your compensation plan with these objectives to ensure that your account managers are motivated to achieve them.
Once you have a clear understanding of your business objectives, you can begin designing the compensation plan. It’s important to keep the plan simple enough so that your AMs feel encouraged (not discouraged) by their compensation model.
Explore similar compensation plans
What industry leaders say
Manage compensation & track commissions with QuotaPath
Deliver visibility, automation, and seamlessness across the entire compensation process.